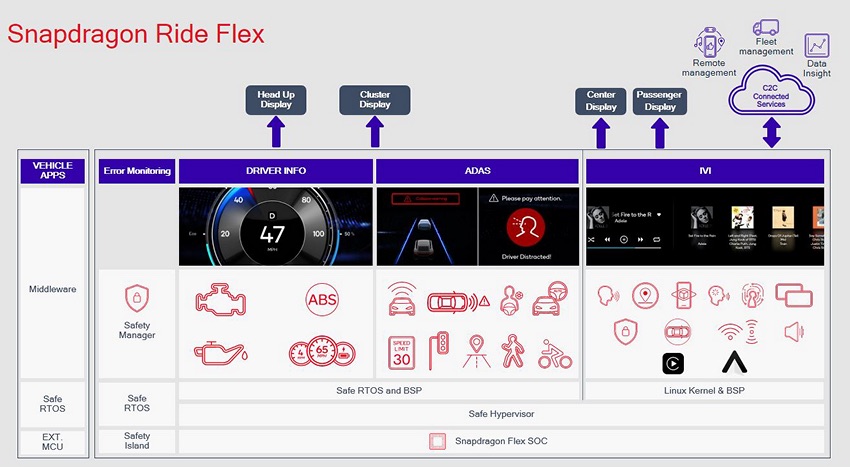
Flex SoC enables a hardware architecture to support isolation, freedom from interference, and quality-of-service (QoS) for specific ADAS functions and comes equipped with a dedicated Automotive Safety Integrity Level D (ASIL-D) safety island.
The chip pre-integrates a software platform that supports multi-operating system operating concurrently, hypervisor enablement with isolated virtual machines, and real-time operating system (OS) with an Automotive Open System Architecture (AUTOSAR) to meet the mixed criticality workload requirements for driver assistance safety systems, digital reconfigurable clusters, infotainment systems, driver monitoring systems (DMS), and park-assist systems.
The device has the Snapdragon Ride Vision stack, which enables ADAS functionality using a front camera to meet regulatory requirements, and multi-modal sensors (multiple cameras, radars, lidars and maps) for enhanced perception that creates an environmental model around the vehicle feeding into vehicle control algorithms.
The Ride Vision stack meets the New Car Assessment Program (NCAP) requirements and Europe’s General Safety Regulations (GSR) while scaling up to higher levels of autonomy.
The Flex SoC family is compatible with the broader portfolio of SoCs within the Snapdragon Digital Chassis Platform.
The family scales from entry-level to premium, high-end central-compute systems, providing the flexibility to automakers to choose the appropriate performance point for their vehicle tiers.
With this capability, automakers are able to realize complex cockpit use-cases, such as integrated instrument clusters with immersive high-end graphics, infotainment and gaming displays, and rear seat entertainment screens, concurrently with latency-critical premium audio experience.
The Flex SoC is designed to be an in-vehicle central-compute platform to power Software Defined Vehicle (SDV) solutions by providing best-in-class high performance, heterogenous safe compute with the ability to execute flexible mixed critical cloud-native workloads.
The in-vehicle compute is complemented by software capable of being deployed on a containerised infrastructure.
The family is supported by a cloud-native automotive software development workflow which includes support for virtual platform simulation that can be integrated as part of in-cloud development operations (DevOps) and machine learning operations (MLOps) infrastructure.







