Dubbed SWOT (Surface Water and Ocean Topography), the international mission‘s satellite took off from Vandenberg in California on 16 December. It is the first to measure all the water on earth both on land and the oceans, and it will do so every 21 days.
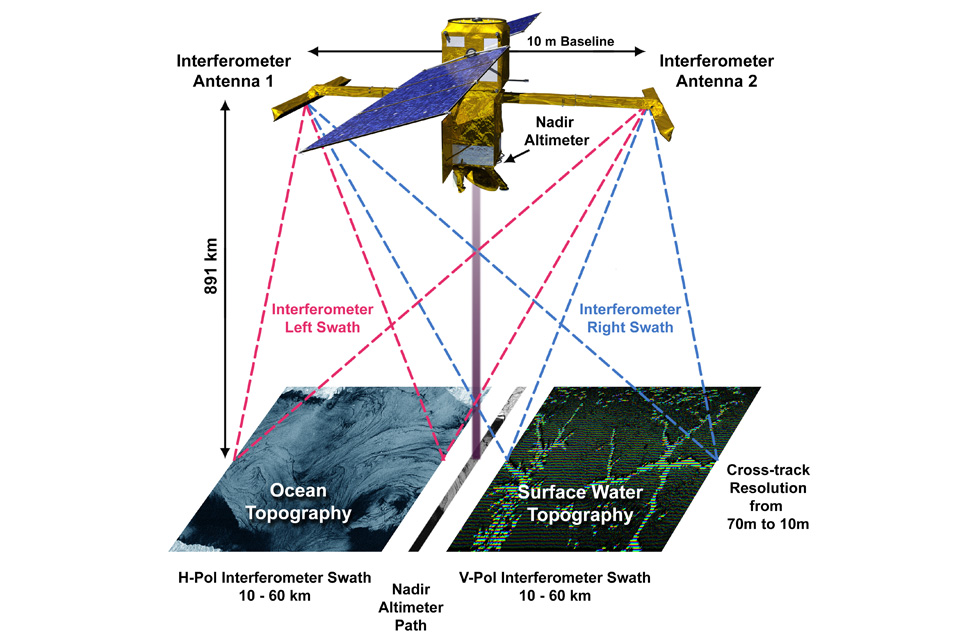
SWOT will use a radar instrument, named KaRIn, that is capable to survey at least 90% of the Earth’s surface. This facility will be used for measuring and monitoring changes in the ocean, lakes, reservoirs, rivers and wetlands.
The goal, highlights the UK Space Agency, is to produce data that will help improve our understanding of climate change, as well as predict and mitigate flood risks around the world.
SWOT is a satellite jointly developed by NASA and the French space agency, CNES, in partnership with the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and UK Space Agency.
The UK Space Agency has provided UK technology company Honeywell with £12.2 million to develop KaRIn’s Ka Band duplexer, which routes vital radar signals around the satellite at a frequency never reached before.
Paul Bates CBE FRS, Professor of Hydrology at the University of Bristol, was part of the team that originally pitched the SWOT concept to NASA 20 years ago, and his team contributed flood hydraulic models during the mission design phase.
“SWOT will transform our ability to track freshwater on planet Earth and currents in the ocean,” said Professor Bates. “For the first time, we will be able to track flood waves moving down river systems and see the rise and fall of water levels in millions of lakes and wetlands worldwide.
“We will not only be able to use these data to make new scientific discoveries, but also to help populations worldwide better manage water hazards and resources.”
Honeywell
The UK Space Agency has provided UK technology company Honeywell with £12.2 million to develop KaRIn’s Ka Band duplexer, which routes vital radar signals around the satellite at a frequency never reached before.
Built in the UK, Honeywell’s Ka Band duplexer is described as a vital part of the KaRIn altimeter on the SWOT satellite, routing radar signals around the satellite and transmitting at a power of 1,500W, allowing KaRIn to measure water levels to better than 2 cm height accuracy at a spatial resolution of 1 km from an orbit height of 891 km above the Earth.
Image: NASA
See also: UK Space Agency backs Clearspace, Astroscale for debris removal missions